What is Forex Trading?
Forex (Foreign Exchange) is the largest and oldest financial market, with a daily trading volume of over USD 7 trillion. It operates 24/7 across global hubs like New York, London, and Tokyo, allowing traders to exchange currencies in pairs.
In forex trading, traders buy one currency while simultaneously selling another, making profits based on exchange rate fluctuations. Unlike stocks or commodities, forex settlements are typically done in cash.
In India, forex trading is regulated by FEMA, allowing trades only in INR pairs. The BSE and NSE offer forex derivative trading, and to start trading, one must open an account with the Currency segment activated.
Trading in Forex
The rise of telecommunications has greatly enhanced forex trading, allowing easy access to currency markets worldwide. Forex trading occurs in currency pairs, such as USD/INR or GBP/USD, where each currency represents a distinct market.
A large portion of forex transactions happens between banks, which play a crucial role in determining currency values. The forex market contributes significantly to global financial liquidity by enabling traders to settle international transactions.
In India, exchanges like NSE, BSE, and MCX offer Currency Futures trading. To participate, traders must open a currency trading account with a broker, and trading takes place from 9 am to 5 pm, with cash settlements and no physical delivery required.

Trading in Forex
The rise of telecommunications has greatly enhanced forex trading, allowing easy access to currency markets worldwide. Forex trading occurs in currency pairs, such as USD/INR or GBP/USD, where each currency represents a distinct market.
A large portion of forex transactions happens between banks, which play a crucial role in determining currency values. The forex market contributes significantly to global financial liquidity by enabling traders to settle international transactions.
In India, exchanges like NSE, BSE, and MCX offer Currency Futures trading. To participate, traders must open a currency trading account with a broker, and trading takes place from 9 am to 5 pm, with cash settlements and no physical delivery required.
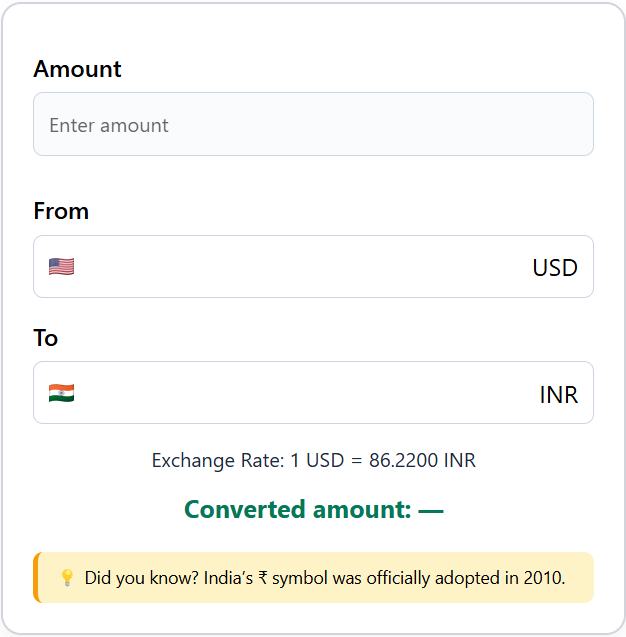
Currency Converter
Easily convert between global currencies with real-time exchange rates. Whether you’re traveling, shopping online, or managing international finances, our currency converter helps you get accurate conversions in seconds.
– Real-time Exchange Rates
– Intuitive Interface
– Searchable Dropdowns
– 100% Free and Secure
Currency Trading Terminologies
Pairs
Currency trading always happens in pairs. There are three types: major pairs, minor pairs, and exotic pairs. Major pairs involve the US Dollar, like USD/JPY. Minor pairs involve currencies from other major economies, like INR/GBP. Exotic pairs feature one major currency and one less common currency, like JPY/NOK (Japanese Yen and Norwegian Krone).
Base Currency and Quote Currency
In a currency pair like INR/JPY, the first currency is the base currency (INR), and the second one is the quote currency (JPY). The base currency is valued at 1, meaning 1 unit of INR is equivalent to 1.60 JPY at the exchange rate.
Pip
A pip is the smallest unit of price movement in a currency pair, often representing a 0.0001 change in value.
Spread
The spread is the difference between the ask and bid price. For example, if the bid is 78.7233 and the ask is 78.7236, the spread is 0.0003.
Bid and Ask Price
The bid price is the price a trader is willing to pay to buy the base currency, while the ask price is what they need to pay to sell it. In a pair like USD/INR quoted as 78.7233/78.7236, buying USD will cost 78.7236 INR, and selling USD will give you 78.7233 INR.
Lot Size
In currency derivatives trading, the minimum quantity of units to buy or sell is called the lot size, much like in stock trading.